‘Array’ vs ‘ArrayList’ in PowerShell
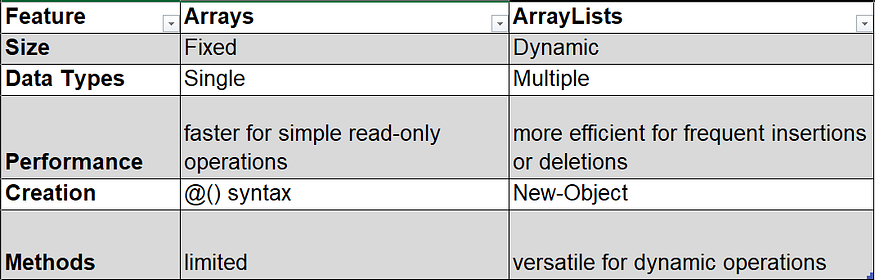
Understanding the differences between arrays and ArrayLists in PowerShell is crucial for effective script development. Arrays offer simplicity and performance for fixed-size collections, while ArrayLists provide flexibility and dynamic sizing. The following table shows the key differences
Array:
$myArray = @(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
- Fixed Size:
Arrays in PowerShell have a fixed size, meaning you need to know the size of the array when you create it. You cannot easily resize an array once it’s created.
- Performance:
Arrays generally have better performance than ArrayLists for simple read and write operations because they are implemented as fixed-size arrays in memory.
- Usage:
Suitable for scenarios where the size of the collection is known and won’t change.
ArrayList:
$myArrayList = New-Object -TypeName System.Collections.ArrayList
$myArrayList.Add(1)
$myArrayList.Add(2)
- Dynamic Size:
ArrayLists, on the other hand, are dynamic in size. They can grow or shrink dynamically as elements are added or removed.
- Methods:
ArrayLists provide additional methods, such as Add(), Insert(), Remove(), and RemoveAt(), making it easier to manipulate the contents.
- Performance:
ArrayLists may have slightly lower performance for simple read and write operations compared to arrays because they use a more complex underlying structure.
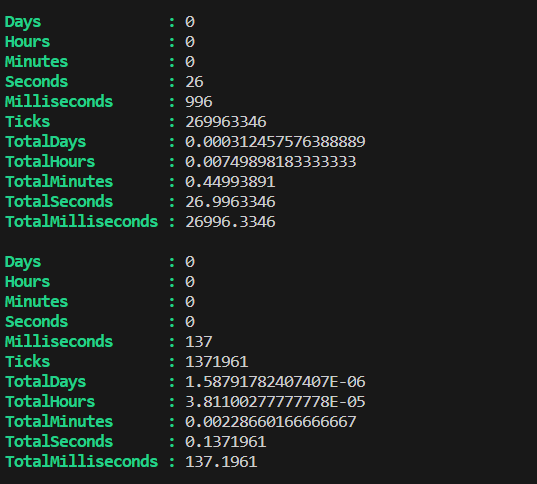
Measure Performace:
Measure-Command can be used to measure the performance of the Array and ArrayList like below
Measure-Command -Expression {@(0..50000).ForEach({$myArray += $_})}
Measure-Command -Expression {@(0..50000).ForEach({$myArrayList.Add($_)})}
Visit https://quizessforyou.com for programming quizzes.